Industrial Laser Marking Systems / Laser Markers
Fibre Laser Marking
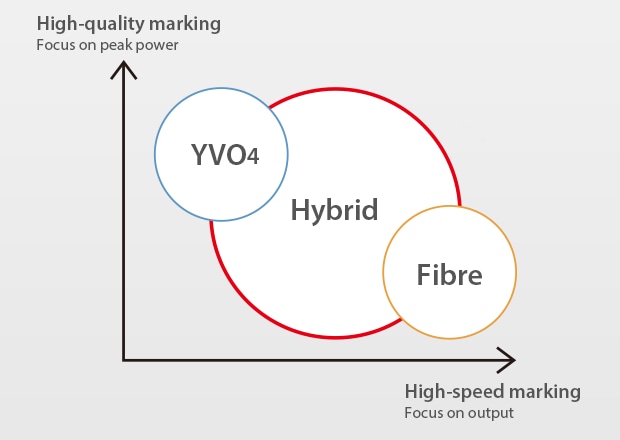
Fibre lasers are solid-state lasers known for their high output power, speed, and ability to deep engrave. Due to this high output power, fibre lasers specialise in engraving, marking, or etching metals at high speeds. However, fibre lasers are known for their heat affect, which can be detrimental when marking plastics or needing precision marks on metals. This is where hybrid laser markers excel, with a combination of fibre and YVO4 technology, hybrid lasers can generate high output powers for metals and high peak power for plastics.
What is a Fibre Laser?
Fibre laser markers have a 1090 nm wavelength, making them IR (infrared) lasers. Fibre lasers can mark a wide range of materials, though they are optimised for metal marking applications. Their high output power makes them perfect for deep engraving applications as well as any marking or processing application with tight cycle time requirements.
Fibre laser markers are actually based on the same technology used for long-distance communication (optical fibres). A laser is efficiently amplified when it travels through an optical fibre, making it possible to produce a high-output fibre laser.
We’re here to provide you with more details.
Reach out today!
The Advantages of Fibre Laser Marking
Why are so many industries using fibre laser marking as part of their operations? Although each use case is unique, manufacturers are benefitting in a number of ways. First, it provides non-contact, high-speed marking with extreme accuracy. As a result, reduced wear on parts and less risk of material distortion are achieved. Fibre laser marking machines stand out for their low maintenance costs and long operational life, reducing downtime.
Fast marking and deep engraving are possible due to the lasers high average power. For manufacturers, a fibre laser engraving machine is particularly advantageous for environments where high-volume production lines demand speed and efficiency. Businesses can avoid costly delays, as the technology of these machines ensures consistent performance, even under continuous use. Additionally, their ability to mark intricate designs, text, or codes in a single pass enhances both product traceability and branding efforts.
What is a Hybrid Laser Marker? - Fibre and YVO4
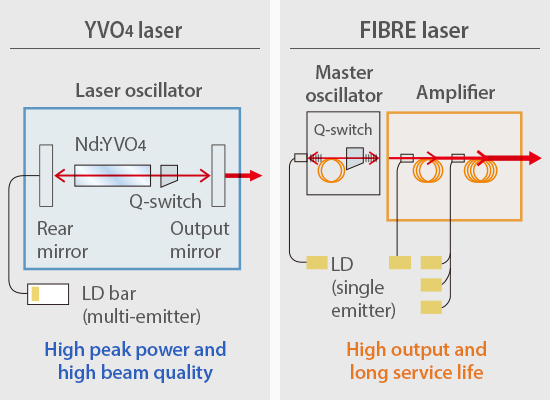
A Hybrid laser marker is a combination of a fibre laser and a YVO4 laser. Fibre lasers are known for their high average power, which is especially important for deep engraving or tight cycle times, while maintaining a long service life. YVO4 laser markers are known for their high beam quality, peak power, and versatility when it comes to marking a wide range of materials. The KEYENCE Hybrid laser has been designed to capitalise on the strengths of both of these laser markers. The built-in oscillator (S-MOPA) provides the advantages of both technologies giving the hybrid a high average power and longer service life, while also giving it the high beam quality, peak power, and overall versatility that the YVO4 laser provides. This makes the hybrid laser marker the most versatile and well rounded laser on the market.
What is S-MOPA & Why is it Important?
Covers the advantages of conventional YVO4 laser markers and fibre laser markers (compared to the conventional KEYENCE model)
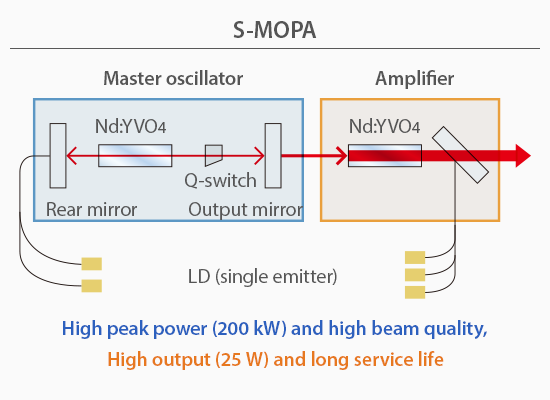
The KEYENCE S-MOPA (Solid-state Master Oscillator Power Amplifier) is a next-generation laser oscillation that combines the high quality and high intensity of YVO4 lasers with the long service life and excellent radiation characteristics of fibre lasers. One unique characteristic of the S-MOPA is its two-stage construction in which a YVO4 laser oscillator (master oscillator) is used to generate the pulse, which is then amplified by a YVO4 amplifier. This makes it possible to amplify the pulse generated by the master oscillator while maintaining the high peak power and high quality of the pulse.
Also, single-emitter pumping laser diodes - an advantage of fibre lasers - are used. This provides lower heat density than the multi-emitter laser diodes (laser diodes that have multiple light emitting surfaces in a single semiconductor chip) of solid state lasers. This enables the KEYENCE S-MOPA to have a long service life even while being a solid state laser.
We’re here to provide you with more details.
Reach out today!

Peak Power: Fibre vs. Hybrid
The main difference between the hybrid and the fibre lasers are their peak powers and their pulse widths. Peak power is the intensity of the light and pulse width is the duration of light. Hybrid lasers have the characteristic of easily creating light with a high peak and short pulse, which they get from the YVO4 technology. Fibre lasers have the characteristic of easily creating light with a low peak and long pulse. When subjecting materials to a laser, the processing results vary greatly depending on the pulse differences.
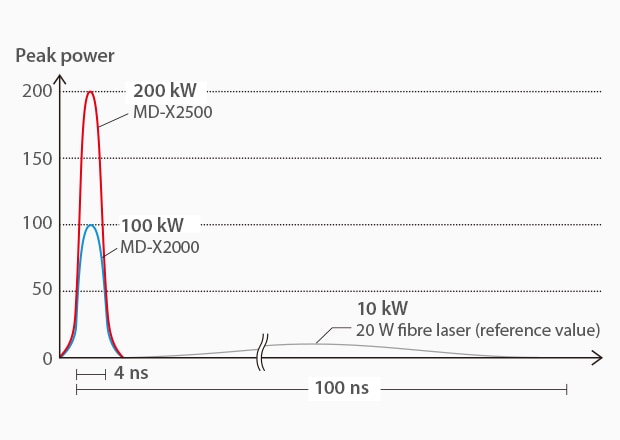
The high peak and short pulse allow the light to have a better reaction with the material with very limited heat effect. This leads to the ability to mark a wider range of materials, especially heat sensitive metals and plastics, with high contrast and much less heat effect. The low peak and long pulse leads to a lot more heat effect on the marked materials, making it much more difficult to mark plastics or heat sensitive material without burning or charring. On the other hand, the low peak and long pulse allows for deep engraving or digging into harder materials with faster cycle times than its counterpart.
Contrast Marking on White Resin

YVO4 laser

Fibre laser
Nickel-Plated Marking
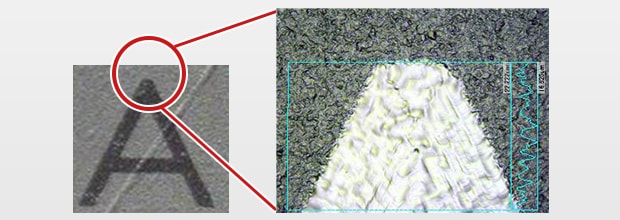
YVO4 laser
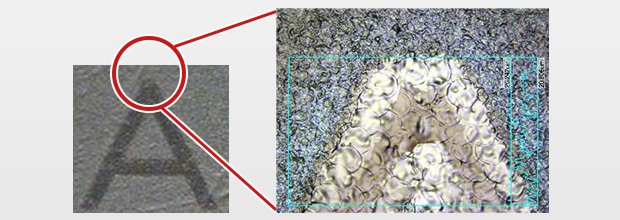
Fibre laser
SUS Engraving
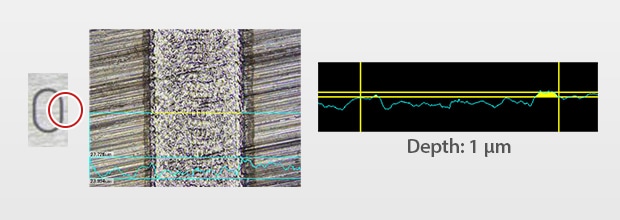
YVO4 laser
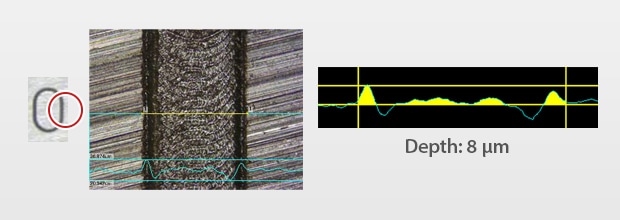
Fibre laser
Beam Quality: Fibre vs. Hybrid
The beam quality of a laser marker is extremely important because it can determine the energy concentration and overall effectiveness of the laser. The quality of a beam is measured with a M2 value, the closer this value is to 1 the higher the quality of the beam. This is also one of the differences between hybrid and fibre laser markers. The YVO4 oscillator in the hybrid laser generates a beam with an M2 value less than 1.3, which is significantly better than the fibre standard around 2.
The reason that this is important is the better the beam quality the more consistent the mark and the greater the depth of focus. Depth of focus is an important factor for basic performance in order to achieve and maintain marking quality. When used in combination with the Z tracking function, this also results in a very high tolerance to height deviation, one of the most common concerns or issues with laser marking in general.
Curious about our pricing?
Click here to find out more.
Marking Versatility: All Laser Comparison
The combination of fibre technology and YVO4 technology makes the hybrid laser one of the most, if not the most, versatile lasers on the market. With S-MOPA, high peak power, short pulse duration, and high beam quality the hybrid laser can mark almost every material. Below shows the comparison of how well UV, Green, Hybrid, Fibre, and CO2 lasers mark a variety of materials.
Material Selection
| Material name | Hybrid Laser Marker MD-X Series |
CO2 Laser Marker ML-Z Series |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Resin | EP (epoxy resin) | very good | good |
| ABS (ABS resin) | very good | possible | |
| PBT | very good | possible | |
| PA | good | good | |
| PC (polycarbonate) | good | good | |
| PP (polypropylene) | good | good | |
| PE (polyethylene) | good | good | |
| PET | not possible | very good | |
| PPS | good | good | |
| PS (polystyrene) | good | good | |
| PI (polyimide) | possible | possible | |
| PVC (polyvinyl chloride) | good | very good | |
| Glass epoxy | good | good | |
| Metal | SUS (stainless steel) | very good | not possible |
| Fe (iron) | very good | not possible | |
| Al (aluminium) | very good | not possible | |
| Ni (nickel) | good | not possible | |
| Cu (copper) | good | not possible | |
| Au (gold) | good | not possible | |
| Other | Ceramic | good | good |
| Si (silicon) | good | possible | |
| Paper | good | very good | |
| Rubber | very good | very good | |
| Glass | not possible | very good | |
| Wood | possible | very good |
Scroll
*The evaluations for the symbols given in the table vary depending on the state and additives of the target as well as on the set conditions. Use this information as typical examples
Fibre Laser Feature: High Power Laser Engraving
A fibre laser engraves by heating the material until a point of vaporisation, leaving an engraved marking behind. Fibre lasers have a much higher output power than conventional laser markers. As a result, they're able to perform most applications at a much faster pace. Choose a fibre laser marker when you need a fast mark or a deep engrave on metal.
How to Choose the Best Fibre Laser Engraving Machine
Choosing your fibre laser engraving machine depends on your production size, intricacy of designs, and type of engraving. Let’s take a deeper look at each.
Production Size
If you have a small production size and parts, you may choose a table-top fibre laser engraver or a desktop laser. These laser systems are not integrated into a process line and require manual changeover, often referred to as "offline" marking.
Alternatively, if you’re involved in mass production or engraving large parts, choose an automated fibre laser engraving machine. Automated laser engravers are integrated into the process line and perform repetitive tasks, often referred to as "inline" marking.
Intricacy of Designs
The type of designs you need your laser to engrave will determine the type of software and beam you require. For those creating custom or elaborate designs, you will need a fibre laser engraving machine with high-quality software that can imitate these designs. Additionally, if you plan to mark on a curved surface or surface that has any change in depth, you will benefit from a laser beam that engraves on 3-axes.
Type of Engraving
If you’re in the market for a laser marker that can engrave deeply or engrave on hard materials, you’ll need a low peak and long pulse laser. On the other hand, if you need higher quality and precision or engraving on sensitive materials, you should opt for a high peak and short pulse.
We’re here to provide you with more details.
Reach out today!

Product Introduction
Automatic Position and Focus Correction 3-Axis Hybrid Laser Marker MD-X Series
Built-in Vision
The MD-X Series contains a camera inside the laser marking head which can automatically identify a target’s shape. The laser marker can then adjust for X, Y, and theta offsets to ensure the marking position is always correct. The marking system is even able to distinguish between parts and mark each part accordingly.
Autofocus Anywhere
The MD-X laser marker comes standard-equipped with a built-in distance sensor that enables automatic focal corrections. Eliminate manual height adjustments due to part variations in a few simple steps.
Data-Driven Analytics
The MD-X uses predictive maintenance to eliminate problems before they occur. In the unlikely event of a marking defect, the laser marker features a wide range of diagnostic tools to identify the root cause and deploy countermeasures.
Get detailed information on our products by downloading our catalogue.
View Catalogue
Differences Between CO2 Laser and Fibre Laser
CO2 lasers and fibre lasers both use infrared range light. However, they process differently. Fibre lasers use a wavelength of 1090 nm, while CO2 lasers use 10x that—a 10600 nm wavelength. Because of the drastic difference in wavelengths, fibre and CO2 lasers are generally purposed for very different applications.
The high heat of CO2 lasers makes them optimal for processing transparent targets that don’t absorb fibre laser light. Likewise, fibre lasers process metals that do not absorb CO2 laser light.
However, these lasers are both excellent for laser cutting. Both a CO2 and fibre laser machine will excel at cutting because of their high output power.
Differences Between UV Laser and Fibre Laser
UV lasers and fibre lasers use different methods for processing; therefore, these lasers are not interchangeable. While the fibre laser uses an infrared laser with a wavelength of 1090 nm for heating materials, UV lasers use a 355 nm UV laser. Additionally, instead of travelling through a fibre, UV lasers travel through two crystals to reach the final beam point.
Because these lasers use different methods, they process completely different materials. Since the 355 nm wavelength of a UV laser is so readily absorbed, it processes material through photolytic degradation or “cold marking.” This allows for high-contrast marking with little to no thermal impact on the product being marked. Because of the lack of heat stress, UV lasers are commonly used on sensitive materials like paper, plastic, resin, and cardboard. They are commonly used for marketing metals in specific industries where surface finish, depth, and material properties of products cannot be compromised.
Fibre Laser Machine Safety
Fibre lasers are classified as Class 4/Class IV lasers by the FDA and IEC. Class 4 means that skin exposure and indirect/direct viewing of a fibre laser are potentially dangerous.
KEYENCE’s Fibre Laser Machine Integrated Safety Measures
Many fibre lasers come with integrated safety measures for preventing harm. KEYENCE’s fibre laser includes a key control, radiation emission warning, a laser shutter, an emergency stop input terminal, a manual reset option , along with redundant safety through a contactor that is ISO 13849-1 compliant.
Key Control
KEYENCE’s fibre laser turns on and off with the turn of a key.
Radiation Emission Warning
A laser radiation emission indicator lights up when the key-operated switch turns the machine on.
Laser Shutter
When the fibre laser is on, a shutter encloses the beam to prevent laser beam emission.
Emergency Stop
The fibre laser includes two input terminals. If one is opened, the laser automatically stops.
Manual Reset
If an error occurs in the laser, the laser must be manually turned back on. The manual control prevents the laser from turning on when an error is not resolved.
ISO 13849-1 Compliance
KEYENCE laser markers can be made ISO 13849-1 compliant and achieve PLe, the highest performance level rating.
Discover more about this product.
Click here to book your demo.
Organisational Safety Measures for Using Fibre Laser Machines
Fibre Laser Machine Location
Always put a warning sign at the entrance of the laser area. The sign will alert all traffic to adhere to laser safety standards. Additionally, ensure there is a local ventilation system if gas is emitted from your laser engraver.
Fibre Laser Machine Protective Clothing and Goggles
Always wear protective clothing and eye protection goggles that cover as much skin as possible when operating a fibre laser. Make sure the protective goggles are specifically made for fibre lasers.
Fibre Laser Machine Safety Management System
Before setting up your laser, appoint a laser safety officer. Your laser safety officer should have prior knowledge and experience with a fibre laser marking machine and related safety.
A Laser Safety Officer is responsible for the following:
- Establishing fibre laser emission prevention measures.
- Setting up the fibre laser location.
- Managing key, protective equipment, and training.
Contact us to learn more about how our advanced technology can help take your business to the next level.
Contact Us